🌙 NodeJS之fs模块学习笔记

🌙 1.fs简介
fs全称file system,文件系统,是NodeJS中最强大的API之一,提供了用于文件系统进行交互的各种API。
🌙 2.使用方式
const fs = require('fs')
fs.readFile('hello.txt', (err, data) => {
if(err) throw err;
console.log(data);
});
2
3
4
5
所有的文件系统操作都具有同步(一般以'Sync'结尾的API)和异步的形式。
异步的形式总是把完成回调作为其最后一个参数。 传给完成回调的参数取决于具体方法,但第一个参数总是预留给异常。 如果操作被成功地完成,则第一个参数会为 null 或 undefined。
const fs = require('fs');
fs.unlink('文件', (err) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log('已成功地删除文件');
});
2
3
4
5
6
当使用同步的操作时,发生的异常会被立即地抛出,可以使用 try…catch 处理,也可以冒泡。
const fs = require('fs');
try {
fs.unlinkSync('文件');
console.log('已成功地删除文件');
} catch (err) {
// 处理错误
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
🌙 3. 创建目录
🌙 3.1 fs.mkdir(path[, options], callback)异步创建
pathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window): 文件目录路径optionsObject (opens new window) | integer (opens new window)recursiveboolean (opens new window) 默认值:false。指示是否要创建父目录。modestring (opens new window) | integer (opens new window) 在 Windows 上不支持, mode -- 权限模式。默认值:0o777(linux系统下:所有人、所属组、其他人可读可写可执行)。
callbackFunction (opens new window)
异步地创建目录。
回调会传入可能的异常、以及创建的第一个目录的路径(如果 recursive 为 true), (err, [path])。
可选的 options 参数可以是整数(指定 mode(权限和粘滞位))、或对象(具有 mode 属性和 recursive 属性(指示是否要创建父目录))。 当 path 是已存在的目录时,调用 fs.mkdir() 仅在 recursive 为 false 时才会导致错误。
/**
* 异步创建文件目录
* */
const fs = require('fs');
fs.mkdir('fsDir', err => {
if(err) throw err;
});
// 必须设置recursive: true 才能创建父目录
fs.mkdir('test/fsDir', {recursive: true}, err => {
if(err) throw err;
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
在 Windows 上,对根目录使用 fs.mkdir()(即使使用遍历)也会导致错误:
fs.mkdir('/', { recursive: true }, (err) => {
// = [Error: EPERM: operation not permitted, mkdir 'C:\']
});
2
3
🌙 3.2 fs.mkdirSync(path[, options])同步创建
pathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)optionsObject (opens new window) | integer (opens new window)recursiveboolean (opens new window) 默认值:false。modestring (opens new window) | integer (opens new window) 在 Windows 上不支持, mode -- 权限模式。默认值:0o777(linux系统下:所有人、所属组、其他人可读可写可执行)。
- 返回: string (opens new window) | undefined (opens new window)
同步地创建目录,参数和异步创建目录少了一个回调函数,其余参数相同。 返回 undefined,或创建的第一个目录的路径(如果 recursive 为 true)。
/**
* 同步创建目录
* */
try {
const dirPath = fs.mkdirSync('test/fsDirSync', { recursive: true });
console.log(dirPath);
} catch (e) {
throw e;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
🌙 3.3 fs.mkdtemp(prefix[, options], callback) 异步创建临时目录
prefixstring (opens new window) 目录名称-前缀。默认会再这个前缀后面接上六位随机的字符,保证创建的临时性目录有唯一性optionsstring (opens new window) | Object (opens new window) 指定编码,参数值为:'utf-8'或者{encoding: 'utf-8'}encodingstring (opens new window) 默认值:'utf8'。
callbackFunction (opens new window)errError (opens new window)directorystring (opens new window)
const fs = require('fs');
const os = require('os');
const path = require('path');
// 获取根目录Temp文件路径
const tmpDir = os.tmpdir();
fs.mkdtemp(path.join(tmpDir, '目录-'), 'utf-8', (err, directory) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(directory);
// 打印类似: /tmp/目录-9jEV66(linux) 或 C:\Users\...\AppData\Local\Temp\目录-9jEV66(windows)
});
// 將临时目录创建到指定目录下
const { sep } = path;
fs.mkdtemp(`testDir${sep}`, (err, directory) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(directory);
// 输出类似 `/tmp/abc123`。
// 新的临时目录会被创建在 /tmp 目录中。
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
nodejs中通过fs.mkdtemp 创建的临时目录会自动删除么? (opens new window)
🌙 3.4 fs.mkdtempSync(prefix[, options])同步创建临时目录
prefixstring (opens new window)optionsstring (opens new window) | Object (opens new window)encodingstring (opens new window) 默认值:'utf8'。
- 返回: string (opens new window) 返回创建的目录路径。
🌙 4.追加文件(不存在则创建文件)
🌙 4.1 fs.appendFile(path, data[, options], callback)异步追加文件
pathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window) | number (opens new window) 文件名或文件描述符。datastring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window)optionsObject (opens new window) | string (opens new window)encodingstring (opens new window) | null (opens new window) 默认值:'utf8'。modeinteger (opens new window) 默认值:0o666。文件权限flagstring (opens new window) 参见文件系统flag的支持 (opens new window)。默认值:'a'。
callbackFunction (opens new window)
异步地追加数据到文件,如果文件尚不存在则创建文件。 data 可以是字符串或 Buffer (opens new window)。
fs.appendFile('文件.txt', '追加的数据', (err) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log('数据已被追加到文件');
});
2
3
4
如果 options 是字符串,则它指定字符编码:
fs.appendFile('文件.txt', '追加的数据', 'utf8', callback);
path 可以指定为已打开用于追加(使用 fs.open() 或 fs.openSync())的数字型文件描述符。 文件描述符不会自动关闭。
fs.open('文件.txt', 'a', (err, fd) => {
if (err) throw err;
fs.appendFile(fd, '追加的数据', 'utf8', (err) => {
fs.close(fd, (err) => {
if (err) throw err;
});
if (err) throw err;
});
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
🌙 4.2 fs.appendFileSync(path, data[, options])同步追加文件
pathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window) | number (opens new window) 文件名或文件描述符。datastring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window)optionsObject (opens new window) | string (opens new window)encodingstring (opens new window) | null (opens new window) 默认值:'utf8'。modeinteger (opens new window) 默认值:0o666。文件权限flagstring (opens new window) 参见文件系统flag的支持 (opens new window)。默认值:'a'。
同步地将数据追加到文件,如果文件不存在则创建该文件。 data 可以是字符串或 Buffer (opens new window)。
try {
fs.appendFileSync('文件.txt', '追加的数据');
console.log('数据已被追加到文件');
} catch (err) {
/* 处理错误 */
}
2
3
4
5
6
如果 options 是字符串,则它指定字符编码:
fs.appendFileSync('文件.txt', '追加的数据', 'utf8');
path 可以指定为已打开用于追加(使用 fs.open() 或 fs.openSync())的数字型文件描述符。 文件描述符不会自动关闭。
let fd;
try {
fd = fs.openSync('文件.txt', 'a');
fs.appendFileSync(fd, '追加的数据', 'utf8');
} catch (err) {
/* 处理错误 */
} finally {
if (fd !== undefined)
fs.closeSync(fd);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
🌙 *5. 打开文件
🌙 5.1 fs.open(path[, flags[, mode]], callback)异步打开文件
pathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)flagsstring (opens new window) | number (opens new window) 参见文件系统flag的支持 (opens new window)。 默认值:'r'。modestring (opens new window) | integer (opens new window) 默认值:0o666(可读写)。callbackFunction (opens new window)errError (opens new window)fdinteger (opens new window) 文件描述符的整数
const fs = require('fs');
fs.open('文件.txt', 'r', (err, dir) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log('打开文件', dir);
// 一般不这样使用而是直接使用 fs.readFile
fs.readFile(dir, (err, data) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(data.toString())
})
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
🌙 5.2 fs.openSync(path[, flags, mode])同步打开文件
pathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)flagsstring (opens new window) | number (opens new window) 参见文件系统flag的支持 (opens new window)。 默认值:'r'。modestring (opens new window) | integer (opens new window) 默认值:0o666(可读写)。- 返回: number (opens new window)返回表示文件描述符的整数。
🌙 5.3 为什么不使用它们?
源码解读:
// fs.open方法
function open(path, flags, mode, callback) {
...
// binding.open方法
binding.open(pathModule.toNamespacedPath(path),
flagsNumber,
mode,
req);
}
// fs.readFile
function readFile(path, options, callback) {
...
path = getValidatedPath(path);
// binding.open方法
binding.open(pathModule.toNamespacedPath(path),
stringToFlags(options.flag || 'r'),
0o666,
req);
}
// fs.write
function writeFile(path, data, options, callback) {
...
// 这里调用了fs.open
fs.open(path, flag, options.mode, (openErr, fd) => {
if (openErr) {
callback(openErr);
} else {
writeFd(fd, false);
}
});
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
从源码中可以看出,一般直接使用fs.readFile等方式直接操作文件即可,因为他们都直接或间接的使用了open方法。
🌙 6. 读取文件
🌙 6.1 fs.readFile(path[, options], callback)异步读取文件
pathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window) | integer (opens new window) 文件名或文件描述符。optionsObject (opens new window) | string (opens new window)encodingstring (opens new window) | null (opens new window) 默认值:null。字符编码flagstring (opens new window) 参见文件系统flag的支持 (opens new window)。默认值:'r'。
callbackFunction (opens new window)errError (opens new window)datastring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) 如果没有指定字符编码,则返回原始的 buffer。
异步地读取文件的全部内容。
fs.readFile('文件名','utf8', (err, data) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(data);
});
2
3
4
fs.readFile() 函数会缓冲整个文件。 若要最小化内存成本,则尽可能选择流式(使用 fs.createReadStream())。
🌙 6.2 fs.readFileSync(path[, options])同步读取文件
pathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window) | integer (opens new window) 文件名或文件描述符。optionsObject (opens new window) | (opens new window)encodingstring (opens new window) | null (opens new window) 默认值:null。字符编码flagstring (opens new window) 参见文件系统flag的支持 (opens new window)。默认值:'r'。
- 返回: string (opens new window) | buffer (opens new window) 返回
path的内容。如果指定了encoding选项,则此函数返回字符串。 否则,返回 buffer。
🌙 7. 写入文件
🌙 7.1fs.writeFile(file, data[, options], callback)异步写入文件
filestring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window) | integer (opens new window) 文件名或文件描述符。datastring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | TypedArray (opens new window) | DataView (opens new window)optionsObject (opens new window) | string (opens new window)encodingstring (opens new window) | null (opens new window) 默认值:'utf8'。modeinteger (opens new window) 默认值:0o666。flagstring (opens new window) 参见文件系统flag的支持 (opens new window)。 默认值:'w'。
callbackFunction (opens new window)
当 file 是文件名时,则异步地写入数据到文件(如果文件已存在,则覆盖文件)。 data 可以是字符串或 buffer。
当 file 是文件描述符时,则其行为类似于直接调用 fs.write()(建议使用)。 参见以下关于使用文件描述符的说明。
如果 data 是 buffer,则 encoding 选项会被忽略。
const data = new Uint8Array(Buffer.from('Node.js 中文网'));
fs.writeFile('文件.txt', data, (err) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log('文件已被保存');
});
2
3
4
5
如果 options 是字符串,则它指定字符编码:
fs.writeFile('文件.txt', 'Node.js 中文网', 'utf8', callback);
不等待回调就对同一个文件多次使用 fs.writeFile() 是不安全的。 对于这种情况,建议使用 fs.createWriteStream() (opens new window)。
🌙 7.2fs.writeFileSync(file, data[, options])同步写入文件
filestring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window) | integer (opens new window) 文件名或文件描述符。datastring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | TypedArray (opens new window) | DataView (opens new window)optionsObject (opens new window) | string (opens new window)encodingstring (opens new window) | null (opens new window) 默认值:'utf8'。modeinteger (opens new window) 默认值:0o666。flagstring (opens new window) 参见文件系统flag的支持 (opens new window)。 默认值:'w'。
返回 undefined。
🌙 8. 拷贝文件
🌙 8.1 fs.copyFile(src, dest[, mode], callback)异步拷贝文件
srcstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window) 要拷贝的源文件名。deststring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window) 拷贝操作的目标文件名。modeinteger (opens new window) 用于拷贝操作的修饰符。默认值:0。callbackFunction (opens new window)
异步地将 src 拷贝到 dest。 默认情况下,如果 dest 已经存在,则覆盖它。 除了可能的异常,回调函数没有其他参数。 Node.js 不保证拷贝操作的原子性。 如果在打开目标文件用于写入后发生错误,则 Node.js 将尝试删除目标文件。
mode 是一个可选的整数,指定拷贝操作的行为。 可以创建由两个或更多个值按位或组成的掩码(比如 fs.constants.COPYFILE_EXCL | fs.constants.COPYFILE_FICLONE)。
fs.constants.COPYFILE_EXCL- 如果dest已存在,则拷贝操作将失败。fs.constants.COPYFILE_FICLONE- 拷贝操作将尝试创建写时拷贝(copy-on-write)链接。如果平台不支持写时拷贝,则使用后备的拷贝机制。fs.constants.COPYFILE_FICLONE_FORCE- 拷贝操作将尝试创建写时拷贝链接。如果平台不支持写时拷贝,则拷贝操作将失败。
const fs = require('fs');
const { COPYFILE_EXCL } = fs.constants;
function callback(err) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log('源文件已拷贝到目标文');
}
// 默认情况下将创建或覆盖目标文件。
fs.copyFile('源文件.txt', '目标文件.txt', callback);
// 通过使用 COPYFILE_EXCL,如果目标文件存在,则操作将失败。
fs.copyFile('源文件.txt', '目标文件.txt', COPYFILE_EXCL, callback);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
🌙 8.2 fs.copyFileSync(src, dest[, mode])同步拷贝文件
srcstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window) 要拷贝的源文件名。deststring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window) 拷贝操作的目标文件名。modeinteger (opens new window) 用于拷贝操作的修饰符。默认值:0。
其余同``fs.copyFile(src, dest[, mode], callback)`
const fs = require('fs');
const { COPYFILE_EXCL } = fs.constants;
// 默认情况下将创建或覆盖目标文件。
fs.copyFileSync('源文件.txt', '目标文件.txt');
console.log('源文件已拷贝到目标文件');
// 通过使用 COPYFILE_EXCL,如果目标文件存在,则操作将失败。
fs.copyFileSync('源文件.txt', '目标文件.txt', COPYFILE_EXCL);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
🌙 9.重命名文件
🌙 9.1 fs.rename(oldPath, newPath, callback)异步重命名文件
oldPathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)newPathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)callbackFunction (opens new window)
异步地把 oldPath 文件重命名为 newPath 提供的路径名。 如果 newPath 已存在,则覆盖它。 除了可能的异常,完成回调没有其他参数。
也可参见 rename(2) (opens new window)。
fs.rename('旧文件.txt', '新文件.txt', (err) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log('重命名完成');
});
2
3
4
🌙 9.2 fs.renameSync(oldPath, newPath, callback)同步重命名文件
oldPathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)newPathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)- 返回
undefined
🌙 10.判断文件
🌙 10.1 fs.access(path[, mode], callback) 异步测试文件权限(存在、读写)
pathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)modeinteger (opens new window) 默认值:fs.constants.F_OK。callbackFunction (opens new window)
测试用户对 path 指定的文件或目录的权限。 mode 参数是一个可选的整数,指定要执行的可访问性检查。 查看文件可访问性的常量 (opens new window)了解 mode 的可选值。 可以创建由两个或更多个值按位或组成的掩码(例如 fs.constants.W_OK | fs.constants.R_OK)。
最后一个参数 callback 是回调函数,调用时会传入可能的错误参数。 如果任何可访问性检查失败,则错误参数会是 Error 对象。 以下示例会检查 package.json 是否存在、以及是否可读或可写。
const file = 'package.json';
// 检查文件是否存在于当前目录中。
fs.access(file, fs.constants.F_OK, (err) => {
console.log(`${file} ${err ? '不存在' : '存在'}`);
});
// 检查文件是否可读。
fs.access(file, fs.constants.R_OK, (err) => {
console.log(`${file} ${err ? '不可读' : '可读'}`);
});
// 检查文件是否可写。
fs.access(file, fs.constants.W_OK, (err) => {
console.log(`${file} ${err ? '不可写' : '可写'}`);
});
// 检查文件是否存在于当前目录中、以及是否可写。
fs.access(file, fs.constants.F_OK | fs.constants.W_OK, (err) => {
if (err) {
console.error(
`${file} ${err.code === 'ENOENT' ? '不存在' : '只可读'}`);
} else {
console.log(`${file} 存在,且可写`);
}
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
🌙 10.2fs.accessSync(path[, mode]) 同步测试文件权限(存在、读写)
pathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)modeinteger (opens new window) 默认值:fs.constants.F_OK
同步地测试用户对 path 指定的文件或目录的权限。 mode 参数是一个可选的整数,指定要执行的可访问性检查。 查看文件可访问性的常量 (opens new window)了解 mode 的可选值。 可以创建由两个或更多个值按位或组成的掩码(例如 fs.constants.W_OK | fs.constants.R_OK)。
如果可访问性检查失败,则抛出 Error。 否则,该方法将返回 undefined。
try {
fs.accessSync('etc/passwd', fs.constants.R_OK | fs.constants.W_OK);
console.log('可以读写');
} catch (err) {
console.error('无权访问');
}
2
3
4
5
6
🌙 10.3 fs.open写入时判断存在是否有效
fs.open('文件', 'wx', (err, fd) => {
if (err) {
if (err.code === 'EEXIST') {
console.error('文件已存在');
return;
}
throw err;
}
writeMyData(fd);
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
🌙 10.4 fs.open读取时判断存在文件是否有效
fs.open('文件', 'r', (err, fd) => {
if (err) {
if (err.code === 'ENOENT') {
console.error('文件不存在');
return;
}
throw err;
}
readMyData(fd);
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
🌙 10.5 fs.existsSync(path) 判断文件是否存在
pathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)- 返回: boolean (opens new window)
如果路径存在,则返回 true,否则返回 false。
详见此 API 的异步版本的文档:fs.exists() (opens new window)。
虽然 fs.exists() 是弃用的,但 fs.existsSync() 不是弃用的。 fs.exists() 的 callback 参数接受的参数与其他的 Node.js 回调的不一致。 fs.existsSync() 不使用回调。
if (fs.existsSync('文件')) {
console.log('该路径已存在');
}
2
3
🌙 11. 监听文件的变化
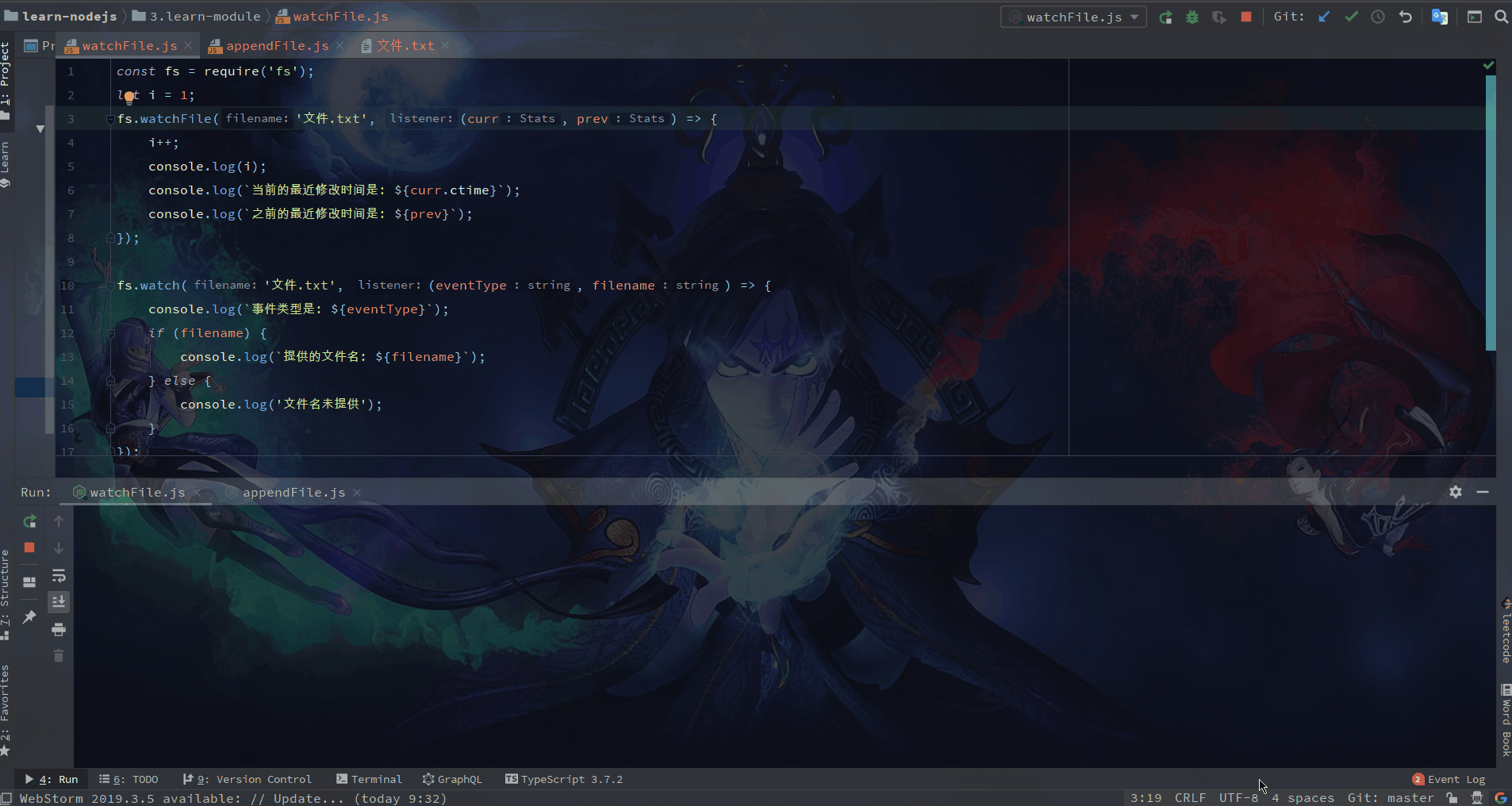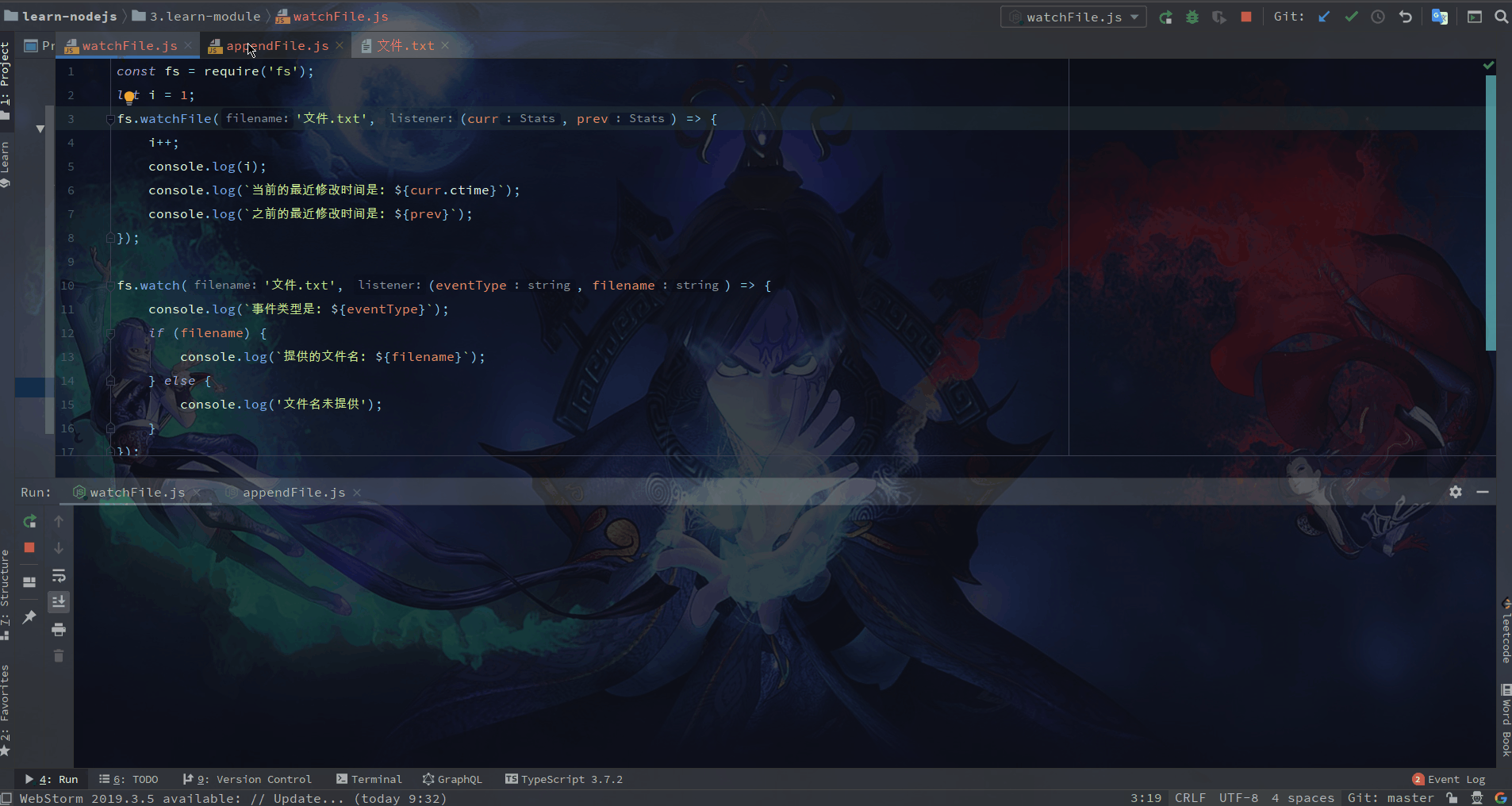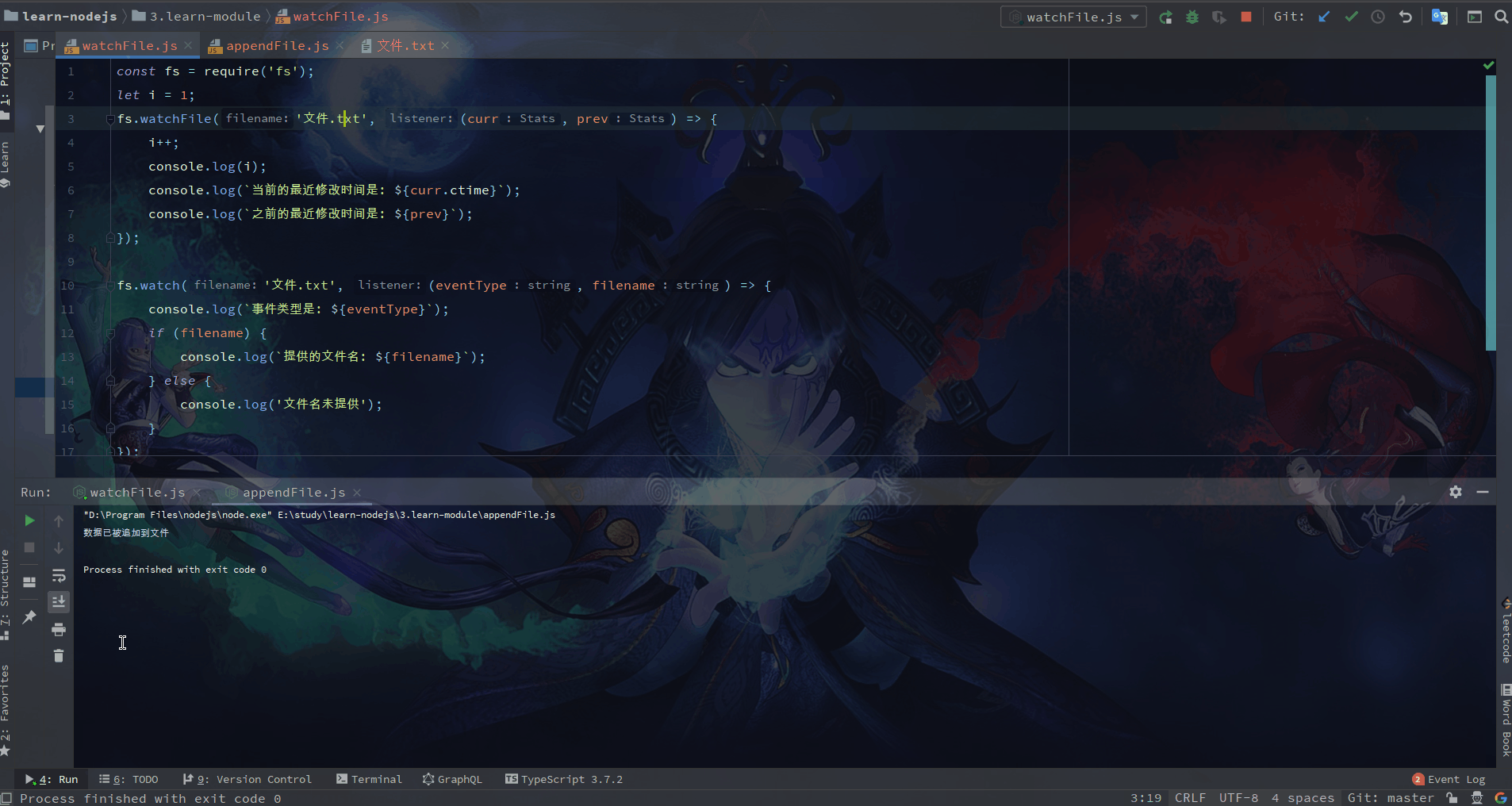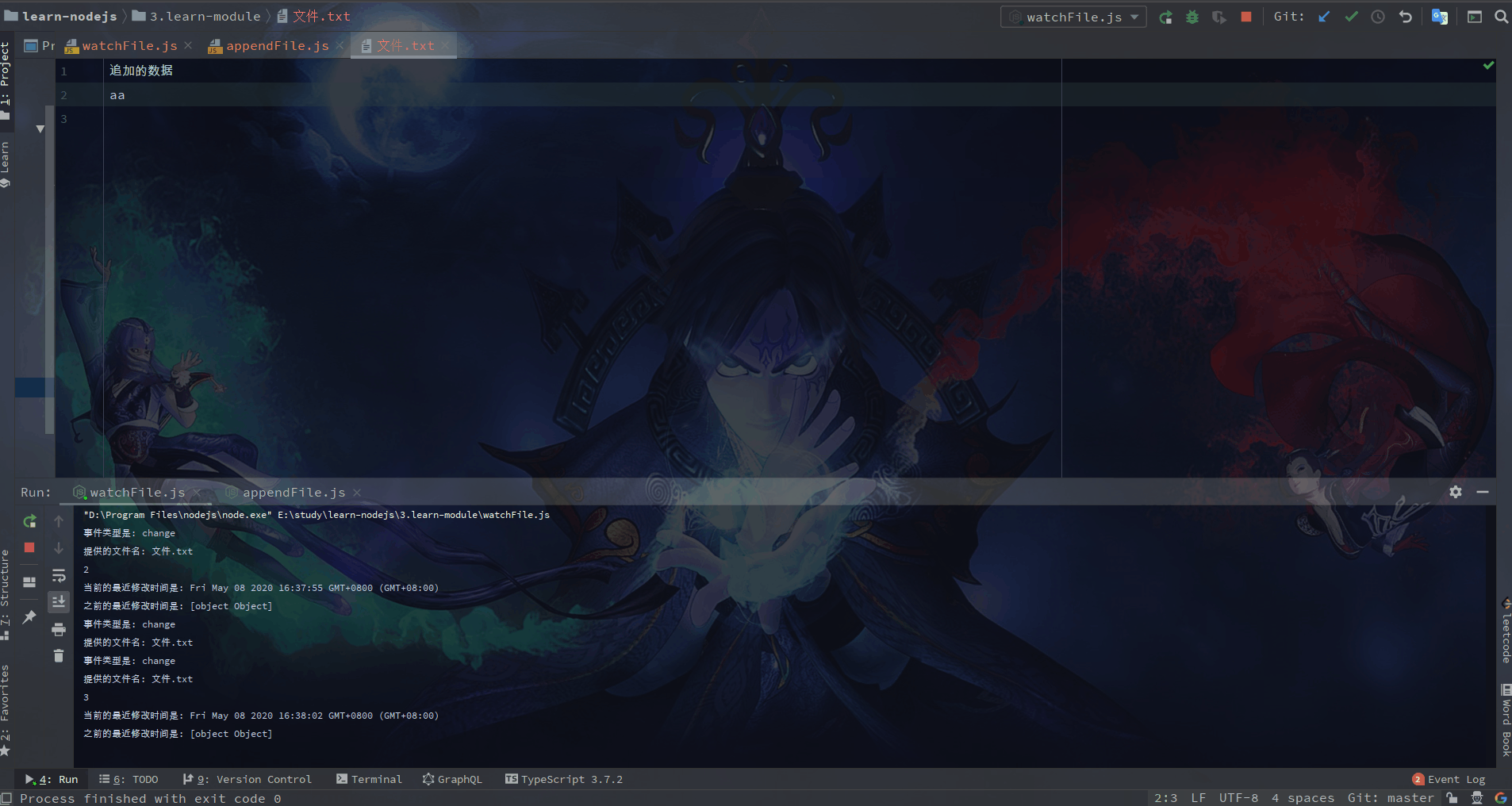
🌙 11.1 fs.watch(filename[, options][, listener])监听文件更改(高效)
filenamestring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)optionsstring (opens new window) | Object (opens new window)persistentboolean (opens new window) 指示如果文件已正被监视,进程是否应继续运行。默认值:true。recursiveboolean (opens new window) 指示应该监视所有子目录,还是仅监视当前目录。这适用于监视目录时,并且仅适用于受支持的平台(参见注意事项 (opens new window))。默认值:false。encodingstring (opens new window) 指定用于传给监听器的文件名的字符编码。默认值:'utf8'。
listenerFunction (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) 默认值:undefined。eventTypestring (opens new window)filenamestring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window)
- 返回: fs.FSWatcher (opens new window)
第二个参数是可选的。 如果 options 传入字符串,则它指定 encoding。 否则, options 应传入对象。
监听器回调有两个参数 (eventType, filename)。 eventType 是 'rename' 或 'change', filename 是触发事件的文件的名称。
fs.watch('somedir', (eventType, filename) => {
console.log(`事件类型是: ${eventType}`);
if (filename) {
console.log(`提供的文件名: ${filename}`);
} else {
console.log('文件名未提供');
}
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
使用 fs.watch() (opens new window) 比 fs.watchFile 和 fs.unwatchFile 更高效。 应尽可能使用 fs.watch 代替 fs.watchFile 和 fs.unwatchFile。
🌙 11.2 fs.watchFile(filename[, options], listener)监听文件更改
filenamestring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)optionsObject (opens new window)bigintboolean (opens new window) 默认值:false。persistentboolean (opens new window) 默认值:true。intervalinteger (opens new window) 默认值:5007。
listenerFunction (opens new window)currentfs.State (opens new window)previousfs.State (opens new window)
监视 filename 的更改。 每当访问文件时都会调用 listener 回调。
options 参数可以省略。 如果提供,则它应该是一个对象。 options 对象可以包含一个名为 persistent 的布尔值,指示当文件正在被监视时,进程是否应该继续运行。 options 对象可以指定 interval 属性,指示轮询目标的频率(以毫秒为单位)。
listener 有两个参数,当前的 stat 对象和之前的 stat 对象:
fs.watchFile('message.text', (curr, prev) => {
console.log(`当前的最近修改时间是: ${curr.mtime}`);
console.log(`之前的最近修改时间是: ${prev.mtime}`);
});
2
3
4
🌙 11.3 fs.unwatchFile(filename[, listener]) 解绑监听器
filenamestring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)listenerFunction (opens new window) 可选的,之前使用fs.watchFile()绑定的监听器。
停止监视 filename 的变化。 如果指定了 listener,则仅移除此特定监听器,否则,将移除所有监听器,从而停止监视 filename。
对未被监视的文件名调用 fs.unwatchFile() 将是空操作,而不是错误。
使用 fs.watch() (opens new window) 比 fs.watchFile() 和 fs.unwatchFile() 更高效。 应尽可能使用 fs.watch() 代替 fs.watchFile() 和 fs.unwatchFile()。
🌙 11.4 为什么推荐fs.watch() (opens new window)
精读《如何利用 Nodejs 监听文件夹》 (opens new window)
原文《How to Watch for Files Changes in Node.js》 (opens new window)
fs.watchFile是通过轮询检测文件变化的,它并不能实时作出反馈,而且只能监听一个文件,存在效率问题。fs.watch通过操作系统提供的文件更改通知机制来监听fs.watch方式取决于底层操作系统,通知文件系统更改的方法如下:(了解一下)- 在 Linux 系统上,使用
inotify(7)(opens new window)。 - 在 BSD 系统上,使用
kqueue(2)(opens new window)。 - 在 macOS 系统上,对文件使用
kqueue(2)(opens new window),对目录使用FSEvents(opens new window)。 - 在 SunOS 系统上(包括 Solaris 和 SmartOS),使用事件端口 (opens new window)。
- 在 Windows 系统上,此特性取决于
ReadDirectoryChangesW(opens new window)。 - 在 Aix 系统上,此特性取决于
AHAFS(opens new window) 必须启动。
仍然可以使用
fs.watchFile(),因为它使用 stat 轮询 ,但这种方法较慢且不太可靠。—— 官方说法- 在 Linux 系统上,使用
const fs = require('fs');
fs.watch(dir, (event, filename) => {
if (filename && event === "change") {
console.log(`${filename} file Changed`);
}
});
2
3
4
5
6
🌙 12.其他
🌙 11.1 文件路径path 参数解读
path string (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window) :大多数 fs 操作接受的文件路径可以指定为字符串、Buffer (opens new window)、或 URL (opens new window) 对象(使用 file: 协议)。
file: URL 始终是绝对路径。
const fs = require('fs');
const fileUrl = new URL('file:///文件');
fs.readFileSync(fileUrl);
2
3
4
🌙 11.2 文件系统标志 (opens new window)
追加
aflag描述 'a'打开文件用于追加。 如果文件不存在,则创建该文件。 'ax'类似于 'a',但如果路径存在,则失败。'a+'打开文件用于读取和追加。 如果文件不存在,则创建该文件。 'ax+'类似于 'a+',但如果路径存在,则失败。'as'打开文件用于追加(在同步模式中)。 如果文件不存在,则创建该文件。 'as+'打开文件用于读取和追加(在同步模式中)。 如果文件不存在,则创建该文件。 读取
rflag描述 'r'打开文件用于读取。 如果文件不存在,则会发生异常。 'r+'打开文件用于读取和写入。 如果文件不存在,则会发生异常。 'rs+'打开文件用于读取和写入(在同步模式中)。 指示操作系统绕过本地的文件系统缓存。 写入
wflag描述 'w'打开文件用于写入。 如果文件不存在则创建文件,如果文件存在则截断文件。 'wx'类似于 'w',但如果路径存在,则失败。'w+'打开文件用于读取和写入。 如果文件不存在则创建文件,如果文件存在则截断文件。 'wx+'类似于 'w+',但如果路径存在,则失败。
🌙 13.高级API
🌙 13.1 异步方法升级为Promise回调:
fs.promises.access测试用户对path指定的文件或目录的权限fs.promises.appendFile异步追加数据fs.promises.copyFile异步拷贝文件fs.promises.mkdir异步创建目录fs.promises.mkdtemp异步创建临时目录fs.promises.open异步打开文件fs.promises.readFile异步读取文件fs.promises.rename异步重命名文件fs.promises.rmdir异步移除文件目录fs.promises.writeFile异步写入文件
const fs = require('fs');
fs.promises.readFile('文件.txt', 'utf8').then(res => {
console.log(res);
});
2
3
4
🌙 13.2 使用Stream流式操作文件
Node.js 流: 你需要知道的一切 (opens new window)
🌙 13.2.1 fs.createReadStream(path[, options])创建可读流
pathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)optionsstring (opens new window) | Object (opens new window)flagsstring (opens new window) 参见文件系统flag的支持 (opens new window)。 默认值:'r'。encodingstring (opens new window) 默认值:null。fdinteger (opens new window) 默认值:null。如果指定了fd,则ReadStream会忽略path参数,并且会使用指定的文件描述符modeinteger (opens new window) 默认值:0o666。autoCloseboolean (opens new window) 默认值:true。emitCloseboolean (opens new window) 默认值:false。startinteger (opens new window) 从文件中读取一定范围的字节,而不是读取整个文件endinteger (opens new window) 默认值:Infinity。从文件中读取一定范围的字节,而不是读取整个文件highWaterMarkinteger (opens new window) 默认值:64 * 1024。fsObject (opens new window) | null (opens new window) 默认值:null。
- 返回: fs.ReadStream (opens new window) 参见可读流 (opens new window)。
const fs=require('fs');
const path=require('path');
let readStream=fs.createReadStream('./test/b.js',{encoding:'utf8'});
//console.log(readStream);
//读取文件发生错误事件
readStream.on('error', (err) => {
console.log('发生异常:', err);
});
//已打开要读取的文件事件
readStream.on('open', (fd) => {
console.log('文件已打开:', fd);
});
//文件已经就位,可用于读取事件
readStream.on('ready', () => {
console.log('文件已准备好..');
});
//文件读取中事件·····
readStream.on('data', (chunk) => {
console.log('读取文件数据:', chunk);
});
//文件读取完成事件
readStream.on('end', () => {
console.log('读取已完成..');
});
//文件已关闭事件
readStream.on('close', () => {
console.log('文件已关闭!');
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
🌙 13.2.2 fs.createWriteStream(path[, options]) 创建可写流
pathstring (opens new window) | Buffer (opens new window) | URL (opens new window)optionsstring (opens new window) | Object (opens new window)flagsstring (opens new window) 参见文件系统flag的支持 (opens new window)。 默认值:'r'。encodingstring (opens new window) 默认值:null。fdinteger (opens new window) 默认值:null。如果指定了fd,则ReadStream会忽略path参数,并且会使用指定的文件描述符modeinteger (opens new window) 默认值:0o666。autoCloseboolean (opens new window) 默认值:true。emitCloseboolean (opens new window) 默认值:false。startinteger (opens new window) 范围 [0,Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER(opens new window)]fsObject (opens new window) | null (opens new window) 默认值:null。
🌙 14.小结
创建目录
fs.mkdir fs.mkdirSync fs.mkdtemp fs.mkdtempSync fs.promises.mkdir fs.promises.mkdtemp1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8追加文件
fs.appendFile fs.appendFileSync fs.promises.appendFile1
2
3
4打开文件
fs.open fs.openSync fs.promises.open1
2
3
4读取文件
fs.readFile fs.readFileSync fs.promises.readFile1
2
3
4写入文件
fs.writeFile fs.writeFileSync fs.promises.writeFile1
2
3
4拷贝文件
fs.copyFile fs.copyFileSync fs.promises.copyFile1
2
3
4重命名文件
fs.rename fs.renameSync fs.promises.rename1
2
3
4判断文件
fs.access fs.accessSync fs.promises.access fs.existsSync1
2
3
4
5
6监听文件
fs.watch fs.watchFile fs.unwatch1
2
3